Staying Secure in a Cyber Pandemic
The Changing Cyber Security Normal
The world changed in 2020 with the outbreak of Covid-19. Countries closed their borders, imposed isolation on their people, drained their financial resources to support their economies. The work life was transformed as well, with a majority of the work force transitioning to home offices to continue their work while maintaining the restrictions. The already growing online life had a major boom during this time.But 2020 will also be remembered as the year that society was transformed with the explosion of cyber security events. Cyber-attackers see the pandemic as an opportunity to step up their criminal activities by exploiting the vulnerability of employees working from home. The negative cyber security impacts of these online changes have resulted in a cyber pandemic. With a wider spread of cyber incidents, protecting assets and infrastructure has become more challenging. Companies are accelerating their digital transformation, and cyber security is now a major concern.
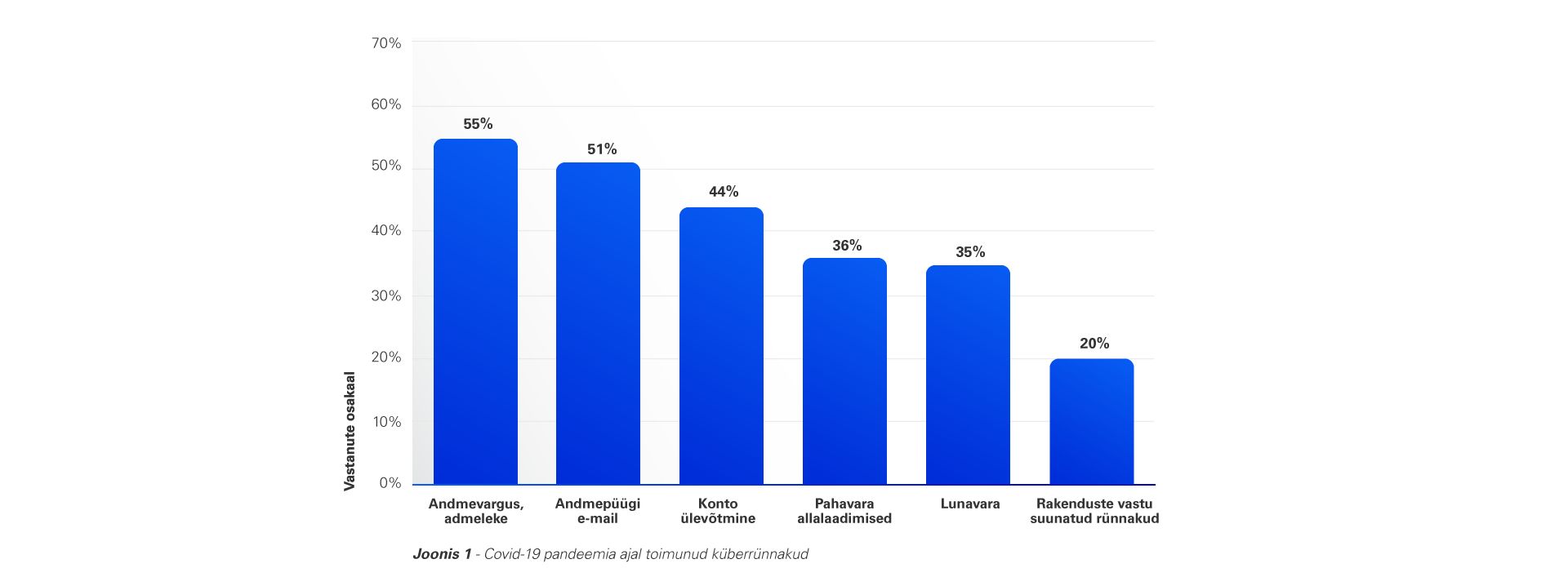
Statista.com highlights the areas in which cyber attacks have increased following the Covid-19 pandemic:
The figure above might seem unusual to a security professional. Application attacks usually occupy a larger portion of the threat landscape. But since the outbreak of covid-19, we are seeing a shift towards attacks leveraging human factors. This could include the susceptibility to phishing and ransomware attacks, misconfigurations due to human error (which are amplified by the rapid adoption of cloud and remote-working tehcnologies), lack of education and expertise or ignorance to mobile threats.
Some of the characteristics of this cyber pandemic include:
But how bad could it really be?
For additional insight, we have compiled the following alarming facts and trends about the cyber pandemic:
- Phishing attacks account for more than 80% of reported security incidents.
(Top cyber security facts, figures and statistics | CSO Online) - On average, a new organization becomes a victim of ransomware every 10 seconds worldwide.
(2021 Cyber Security Report | Checkpoint) - 95% of cyber security breaches are caused by human error.
(Cybint) - The world faces over 100,000 malicious websites and 10,000 malicious files daily.
(2021 Cyber Security Report | Checkpoint) - There were huge increases in the number of attacks against remote access products. Citrix attacks surged by a whopping 2,066%, Cisco attacks went up by 41%, VPN attacks spiked by 610%, and RDP hits increased by 85%.
(2021 Cyber Security Report | Checkpoint) - 46% of organizations had at least one employee download a malicious mobile application.
(2021 Cyber Security Report | Checkpoint) - 86.2% of surveyed organizations were affected by a successful cyber-attack
(CyberEdge Group 2021 Cyberthreat Defense Report) - 87% of organization have experienced an attempted exploit of an already-known, existing vulnerability.
(2021 Cyber Security Report | Checkpoint) - 56% of companies in the US have dealt with a data breach.
(2021 Thales Data Threat Report) - 6 out of 10 companies have over 500 passwords that never expire.
(2021 Varonis Financial Services Data Risk report) - Small businesses are much more likely to be targeted, accounting for over 50% of all breaches. This is an almost 100% increase from last year, when they were the victims just 28% of the time.
(Verizon 2021 Data Breach Investigations Report) - In 2021, the average global cost to remediate a ransomware attack rose to $1.5 million, more than double the previous year’s average ($761,106).
(The State of Ransomware 2021 | Sophos) - In 2021, a single honeypot logged more than 7 billion attacks.
(F-Secure Attack Landscape H1 2021) - More than three-quarters of IT security professionals believe a successful cyber attack is imminent in 2021.
(CyberEdge Group 2021 Cyberthreat Defense Report)
Figure 2 - Enduring from home: COVID-19’s impact on business security report | MalwareBytes
Maintaining Our Security
Today’s dynamically evolving cyber threat landscape requires us to elevate our security habits, practices, procedures and protocols. There is now a need for the security practices to be tailored and fine-tuned to protect against attacks of the new world. To conclude, we have listed some of the safety practices to follow in this cyber pandemic.
- Secure your remote access - Employees working remotely should have anti-virus and malware protections on all systems; Employers should consider providing these protections for personal employee systems accessing corporate resources to keep their own infrastructure secure. Multi-factor authentication should be enforced for all remote access, where possible.
- Improve security education and awareness - There is an increasing need for us to stay up to date with the evolving and changing nature of cyber-attacks. Businesses should implement security awareness programs and also consider simulating phishing campaigns for their employees to get more detailed results on their human security posture.
- Secure your home network - More people than ever are working from home, and it is essential to keep our home network secure. We should ensure our home Wi-Fi network is protected with a strong password and proper protections are in place on all home devices. Consider using a VPN.
- Develop a vulnerability management program - An official vulnerability management program detailing asset inventory, patch status and protection levels can go a long way in a cyber pandemic. Companies should identify IT system weaknesses and patch the most critical vulnerabilities as soon as possible. Detective and investigative protections like SIEM should be in place.
- Prepare for attacks; consider penetration testing - It is advisable for businesses to consider going one step forward and run penetration tests on their assets to get a more accurate insight into their security posture. In these high-risk times, companies should carry out frequent cyber crisis simulation exercises to prepare their response to a cyber-attack.
- Leverage intelligence techniques - Businesses should encourage proactive use of cyber threat intelligence to identify relevant indicators of attacks (IOC) and address known attacks.
- Renew business continuity and crisis plans
Businesses are encouraged to update their business continuity plans according to modern day work and cyber-attack scenarios.
Jagjit Singh
Cyber Security Expert
Latest articles

Why Purple Teaming is the Missing Link in Modern Cybersecurity
In today’s cybersecurity landscape, most organizations are caught between two realities: they kn..

Reflections from the Field - A Red Team’s Perspective on Cybersecurity in Estonia
Over the past several years, our red team has conducted extensive offensive security assessments..
KPMG Expert: AI Solutions for Automating Routine Processes Deliver the Quickest Returns
By implementing artificial intelligence, the quickest returns are achieved thro..

KPMG IT Expert: Practitioner-Trainers Make Training Engaging and Practical
IT or cyber security training is more engaging when delivered by trainers who a..

Your Partners’ Weaknesses Can Affect Your Own Security
When planning your cyber defence strategy, it’s crucial to recognise that vulne..
Bolstering Cyber Resilience with High-Quality Red Teaming
The escalating complexity and frequency of cyberattacks pose a critical risk to the stability of f..
Turn threats into opportunities
Provide a safe and sustainable business environment for your company. We help build a resilient and reliable digital landscape, even in the face of changing threats.

KPMG Baltics OÜ
+372 626 8700cyber@kpmg.ee
Ahtri 4, 10151 Tallinn, Estonia
Contact us
${i18n('ask_more')}
Analysis of employee awareness
Analysis of employee awareness focuses on mapping the skills and increasing the competencies of the weakest link in cyber security: the users, the employees.
${i18n('ask_more')}
Threat assessment
Threat assessment is a tactical and technical service that allows a company to get a quick overview of external threats.
${i18n('ask_more')}
Maturity assessment
Maturity assessment helps plan IT investments and design further steps to mitigate vulnerabilities and ensure better security.